name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse <div class="my-header"><span> <a href="/training-material/topics/statistics" title="Return to topic page" ><i class="fa fa-level-up" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> <a href="https://github.com/galaxyproject/training-material/edit/main/topics/statistics/tutorials/image_learner/slides.html"><i class="fa fa-pencil" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> </span></div> <div class="my-footer"><span> <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTN-60px.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" style="height: 40px;"/> </span></div> --- <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTNLogo1000.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" class="cover-logo"/> <br/> <br/> # Gleam Image Learner - Validating Skin Lesion Classification on HAM10000 <br/> <br/> <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> <ul class="text-list"> <li> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/khaivandangusf2210/" class="contributor-badge contributor-khaivandangusf2210"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/khaivandangusf2210?s=36" alt="Khai Van Dang avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Khai Van Dang</a> <li> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/paulocilasjr/" class="contributor-badge contributor-paulocilasjr"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/paulocilasjr?s=36" alt="Paulo Cilas Morais Lyra Junior avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Paulo Cilas Morais Lyra Junior</a> <li> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/qchiujunhao/" class="contributor-badge contributor-qchiujunhao"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/qchiujunhao?s=36" alt="Junhao Qiu avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Junhao Qiu</a> <li> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/jgoecks/" class="contributor-badge contributor-jgoecks"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/jgoecks?s=36" alt="Jeremy Goecks avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Jeremy Goecks</a></li> </ul> </div> </div> <!-- modified date --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 8em;"> <i class="far fa-calendar" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">last_modification</span> Updated: <i class="fas fa-fingerprint" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">purl</span><abbr title="Persistent URL">PURL</abbr>: <a href="https://gxy.io/GTN:S00140">gxy.io/GTN:S00140</a> </div> <!-- other slide formats (video and plain-text) --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 5em;"> <i class="fas fa-file-alt" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">text-document</span><a href="slides-plain.html"> Plain-text slides</a> | </div> <!-- usage tips --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 2em;"> <strong>Tip: </strong>press <kbd>P</kbd> to view the presenter notes | <i class="fa fa-arrows" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">arrow-keys</span> Use arrow keys to move between slides </div> ??? Presenter notes contain extra information which might be useful if you intend to use these slides for teaching. Press `P` again to switch presenter notes off Press `C` to create a new window where the same presentation will be displayed. This window is linked to the main window. Changing slides on one will cause the slide to change on the other. Useful when presenting. --- ### <i class="far fa-question-circle" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">question</span> Questions - How do we validate GLEAM's Image Learner against a published benchmark on HAM10000? - How do we set up a balanced train/validation/test split for multi-class image classification? - How do we interpret accuracy, weighted precision/recall, and weighted F1 for imbalanced medical imaging datasets? --- ### <i class="fas fa-bullseye" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">objectives</span> Objectives - Prepare a balanced HAM10000 subset and perform a stratified 70/10/20 train/validation/test split. - Train an Image Learner model using a pretrained CaFormer S18 384 backbone. - Evaluate performance using accuracy and weighted precision/recall/F1, and inspect confusion patterns. --- # Introduction to GLEAM Image Learner and Galaxy - **Galaxy**: A web-based platform for data-intensive biomedical research, enabling users to run tools and workflows without coding. - **GLEAM Image Learner**: A no-code deep learning tool for image classification in Galaxy that automates model training and evaluation. - **Goal**: Validate Image Learner on the HAM10000 benchmark with a balanced split and clear, reproducible metrics. ??? GLEAM Image Learner simplifies deep learning by automating tasks like data preprocessing, model training with transfer learning, and comprehensive evaluation. In this tutorial, we will explore how Image Learner can be used within Galaxy to build reliable image classifiers, using the HAM10000 skin lesion dataset as a case study. --- # Use Case: Skin Lesion Classification with HAM10000 - **Dataset Source**: HAM10000 (Human Against Machine with 10,000 training images). - **Tutorial Dataset**: Preprocessed, balanced subset following Shetty et al. (2022). - **Objective**: Train and evaluate a multi-class classifier across seven lesion types. 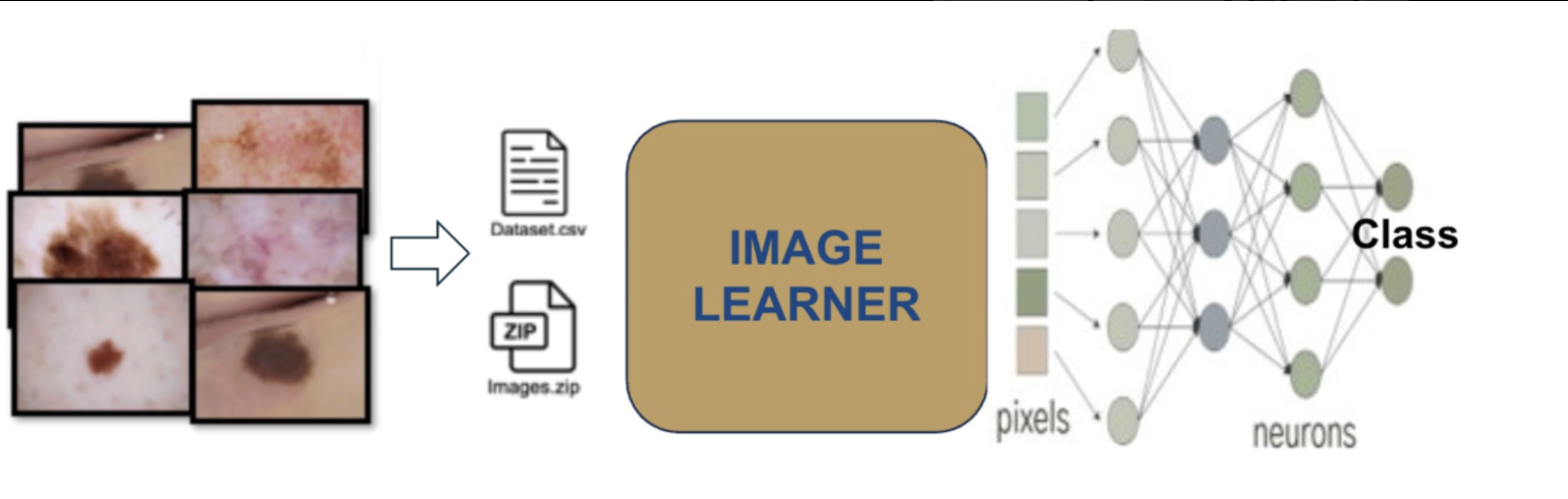 --- # Dataset Preprocessing (Balanced Subset) - **Step 1: Selection**: 100 images per class from the original HAM10000 dataset. - **Step 2: Resizing**: All images resized to 96×96 pixels and stored as PNG. - **Step 3: Augmentation**: Horizontal flips to double each class to 200 images. - **Result**: 1,400 total images (200 × 7 classes), balanced across classes. --- # Balanced Dataset Composition | Lesion Type | Count | Percentage | |---|---|---| | Melanocytic nevus (nv) | 200 | 14.3% | | Melanoma (mel) | 200 | 14.3% | | Basal cell carcinoma (bcc) | 200 | 14.3% | | Actinic keratosis (akiec) | 200 | 14.3% | | Benign keratosis (bkl) | 200 | 14.3% | | Dermatofibroma (df) | 200 | 14.3% | | Vascular lesion (vasc) | 200 | 14.3% | | **Total** | **1,400** | **100%** | --- # Data Augmentation Strategy - **Horizontal Flip Augmentation**: - Creates additional training samples by flipping images - Helps model learn orientation-invariant features - Effectively doubles training set size - Applied during preprocessing to build a balanced dataset 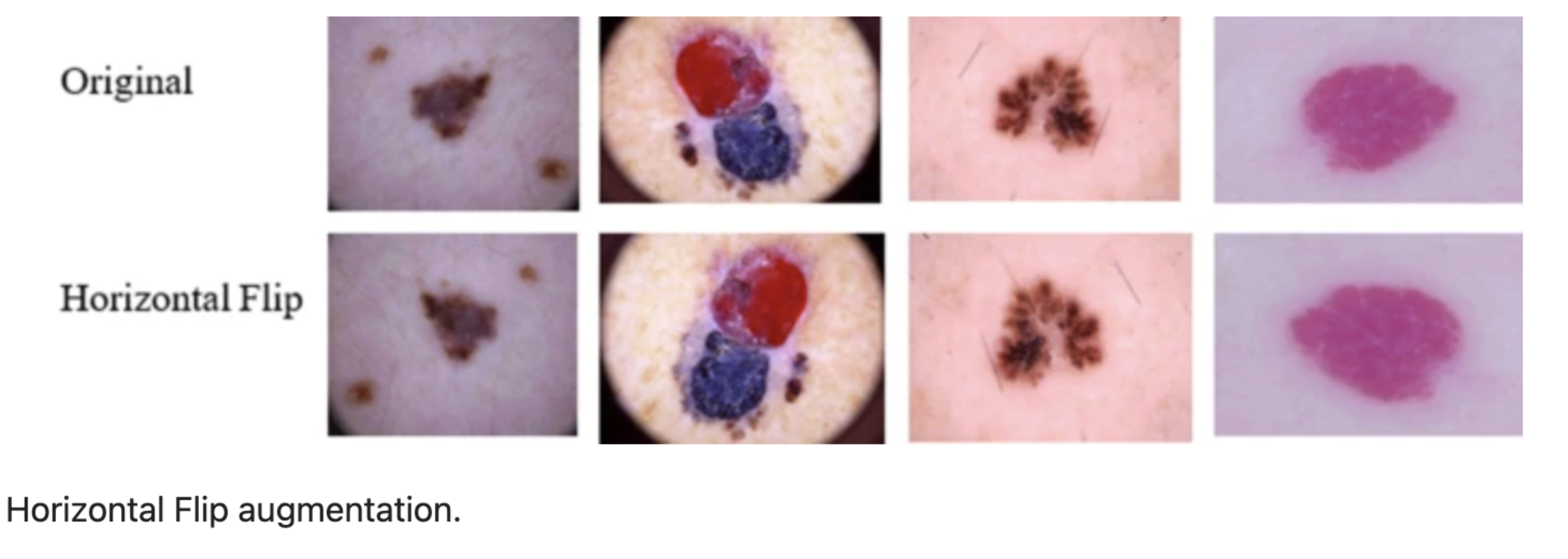 *Adapted from Shetty et al., 2022 ([Scientific Reports 12, 18134](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-22644-9))* --- # Transfer Learning with Image Learner - **Pre-trained Models**: Leverage models trained on ImageNet - **Fine-tuning**: Adapt pre-trained features to skin lesion classification - **Benefits**: - Requires fewer training samples - Trains faster than from scratch - Achieves better performance - Especially effective for medical imaging --- # Image Learner in Galaxy - **GLEAM Image Learner Tool**: - Available on Galaxy: [Galaxy Main](https://usegalaxy.org/) and [https://cancer.usegalaxy.org](https://cancer.usegalaxy.org) - Automates training and evaluation of deep learning models - Outputs trained model and comprehensive performance report - **Key Features**: - Automatic image preprocessing (resizing, normalization) - Transfer learning with multiple model architectures - Data augmentation options - Detailed evaluation metrics and visualizations --- # Model Configuration | Parameter | Value | Rationale | |---|---|---| | Task Type | Multi-class classification | Seven lesion classes | | Model | CAFormer S18 384 | Efficient transformer-based architecture | | Epochs | 30 | Sufficient for convergence | | Batch Size | 32 | Balances memory and stability | | Data Split | Stratified 70/10/20 | Train/validation/test | --- # Running Image Learner 1. **Upload Data**: - images_96.zip (1,400 images - 200 per class) from Zenodo - image_metadata_new.csv (class labels and metadata) - [Zenodo link](https://zenodo.org/records/17114688) 2. **Run Image Learner**: - Input images: images_96.zip - Input metadata: image_metadata_new.csv - Task: Classification - Model: CAFormer S18 384 - Configure parameters as shown 3. **Evaluate Model**: - Use Image Learner's report to assess performance - Analyze ROC-AUC curves and confusion matrix --- # Image Learner Model Report - **Interactive HTML Report**: - **Config & Overview**: Dataset composition, metrics, and configuration - **Training & Validation**: Learning curves and validation diagnostics - **Test Results**: Final metrics, confusion matrix, ROC/PR curves 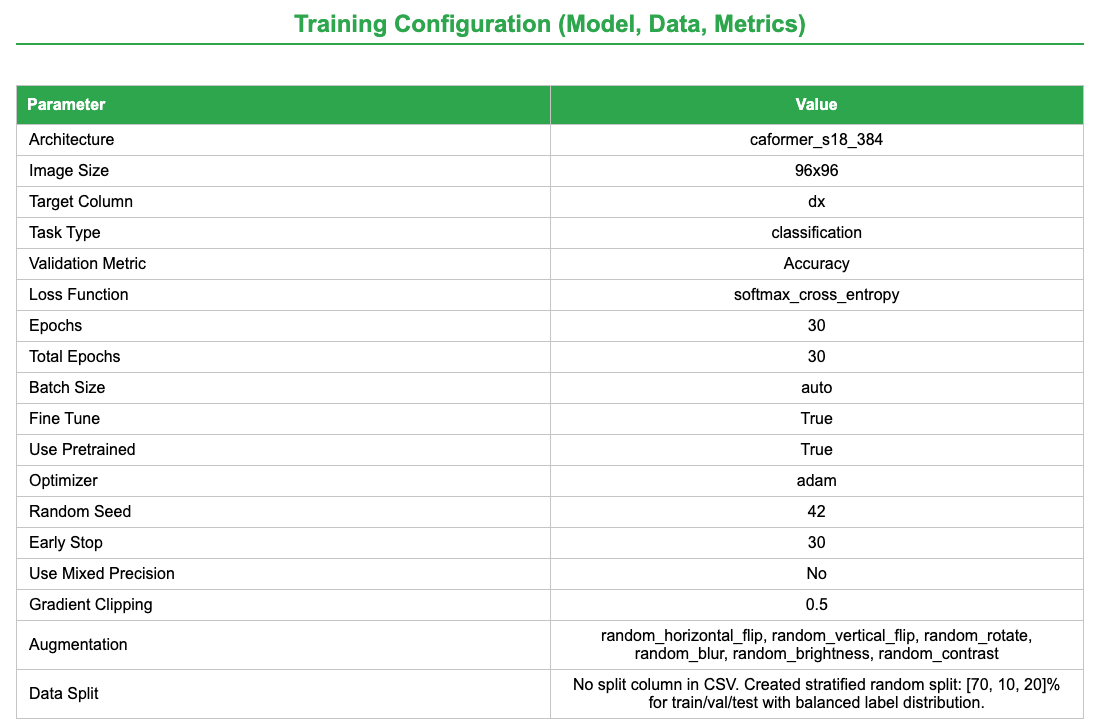 --- # Training Performance 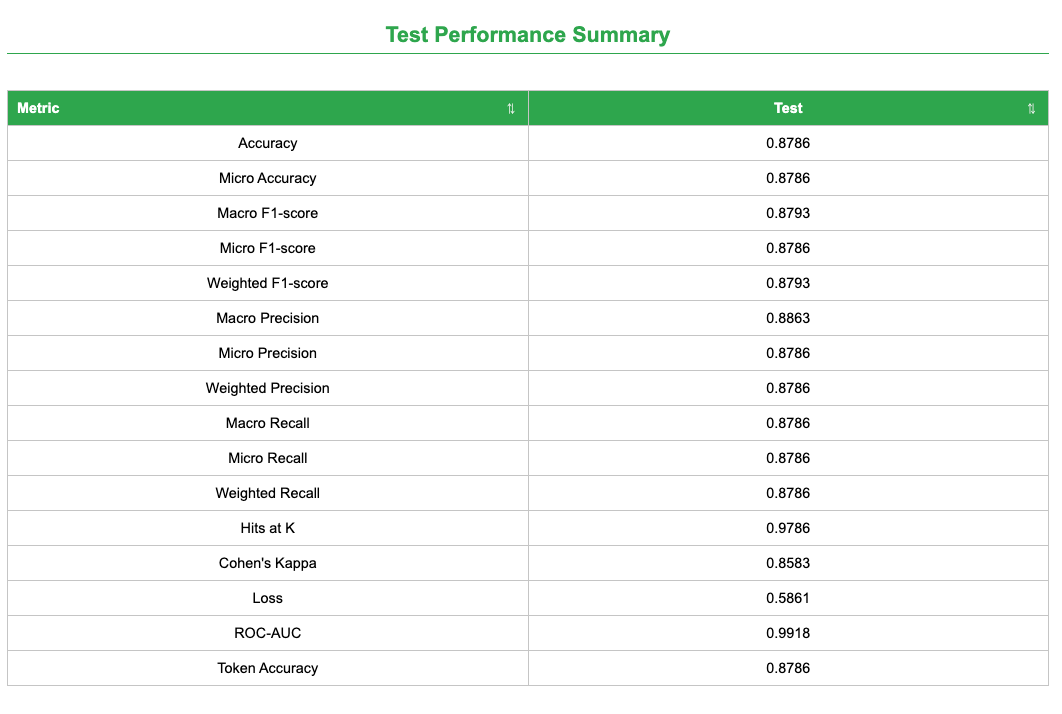 - Monitor training and validation metrics - Identify potential overfitting - Assess convergence --- # Test Results and Diagnostics - **Test Performance Summary**: Accuracy and weighted precision/recall/F1 on the balanced split. - **Classification Diagnostics**: Confusion matrix, ROC/PR curves, and confidence distributions. - **Per-class Metrics**: Heatmap view of precision, recall, F1, and related scores by lesion type.  --- # Confusion Matrix  - **Diagonal**: Correct predictions - **Off-diagonal**: Misclassifications - Identifies which classes are confused with each other - Useful for understanding model limitations --- # Comparison with Shetty et al. (2022) Reference: Shetty et al., 2022 ([Scientific Reports 12, 18134](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-22644-9)) | Metric | Shetty et al., 2022 (CNN) | Image Learner (this tutorial) | |---|---:|---:| | Accuracy | 0.94 (94%) | 0.87 (87%) | | Weighted Precision | 0.88 (88%) | 0.87 (87%) | | Weighted Recall | 0.85 (85%) | 0.87 (87%) | | Weighted F1-Score | 0.86 (86%) | 0.87 (87%) | - Image Learner shows slightly lower accuracy but higher weighted precision/recall/F1. - Differences can reflect model architecture and training/evaluation details. --- # Conclusion - **Key Takeaways**: - Prepared a balanced HAM10000 subset with horizontal-flip augmentation. - Trained a CaFormer-based Image Learner model with a 70/10/20 split. - Evaluated performance using accuracy and weighted precision/recall/F1 plus diagnostics. - **Why Image Learner?** - No coding required - accessible to all researchers - Automates preprocessing, training, and evaluation - Produces publication-ready results and visualizations - Enables rapid experimentation with different models --- ## Thank You! This material is the result of a collaborative work. Thanks to the [Galaxy Training Network](https://training.galaxyproject.org) and all the contributors! <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> <table class="contributions"> <tr> <td><abbr title="These people wrote the bulk of the tutorial, they may have done the analysis, built the workflow, and wrote the text themselves.">Author(s)</abbr></td> <td> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/khaivandangusf2210/" class="contributor-badge contributor-khaivandangusf2210"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/khaivandangusf2210?s=36" alt="Khai Van Dang avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Khai Van Dang</a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/paulocilasjr/" class="contributor-badge contributor-paulocilasjr"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/paulocilasjr?s=36" alt="Paulo Cilas Morais Lyra Junior avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Paulo Cilas Morais Lyra Junior</a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/qchiujunhao/" class="contributor-badge contributor-qchiujunhao"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/qchiujunhao?s=36" alt="Junhao Qiu avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Junhao Qiu</a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/jgoecks/" class="contributor-badge contributor-jgoecks"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo" width="36" height="36"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/jgoecks?s=36" alt="Jeremy Goecks avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /> Jeremy Goecks</a> </td> </tr> <tr class="reviewers"> <td><abbr title="These people reviewed this material for accuracy and correctness">Reviewers</abbr></td> <td> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/shiltemann/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-shiltemann"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/shiltemann?s=36" alt="Saskia Hiltemann avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/paulocilasjr/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-paulocilasjr"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/paulocilasjr?s=36" alt="Paulo Cilas Morais Lyra Junior avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a><a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/anuprulez/" class="contributor-badge contributor-badge-small contributor-anuprulez"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/anuprulez?s=36" alt="Anup Kumar avatar" width="36" class="avatar" /></a></td> </tr> </table> </div> </div> <div style="display: flex;flex-direction: row;align-items: center;justify-content: center;"> <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTNLogo1000.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" style="height: 100px;"/> </div> Tutorial Content is licensed under <a rel="license" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/">Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License</a>.<br/>